A computer is an electronic device that can receive, store, process, and output data. It is a machine that can perform a variety of tasks and operations, ranging from simple calculations to complex simulations and artificial intelligence.
Micro Computers are mainly single-user computers and have comparatively lesser storage and speed than other computers. The first microcomputer was built with 8-bit microprocessor chips as these computers use microprocessors as CPU. Laptops, smartphones, desktop computers, etc. are all examples of microcomputers. These computers are made for everyday tasks like browsing the web and using programs like Microsoft Office MS Word etc.
Midrange computers or Mini-computers are multi-user computers designed in a way so as to entertain multiple users simultaneously. Small businesses and firms use these computers for their specific purposes. For example: a company or organization may use mini computers to look after the employee directory which may handle the payment history of its employees and any schools may use them to keep records of the students or for admission purposes.
Mainframe Computers are also not designed for single users, rather it is a multi-user computer that can handle thousands of users all at once. Large industries and government organizations utilize these computers to facilitate their business operations by storing substantial volumes of data. Banks and insurance companies use these computers to store the data of their customers, their policies, etc.
Super Computer is the fastest type of computer amongst all and is also the most expensive. They can store a large number of data and can perform the most complex tasks within seconds. They can also execute millions of instructions per second. These computers are designed specifically to handle...
Supercomputers are also used by NASA for their Satellite launching and specific tasks such as weather forecasting, space research, and more.
Workstations are single-user computers and have more powerful microprocessors than a microcomputer. When it comes to speed and storage capacity, it comes between a personal computer and a mini-computer. The most common uses of a workstation are desktop publishing, engineering designs.
These are specialized computers that are built into other devices such as cars, appliances, and medical equipment to control their operations and perform specific functions.
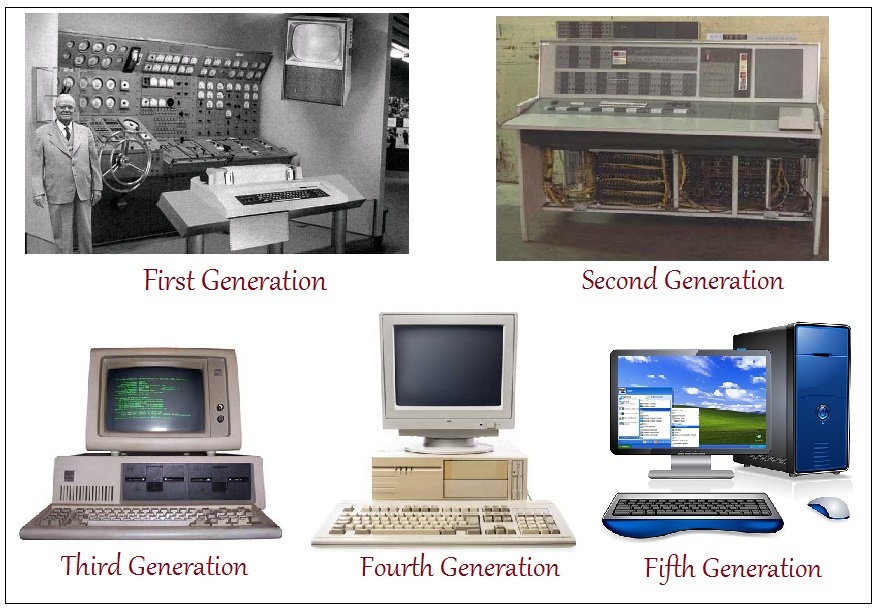

The 1st Generation Computers were introduced using the technology of vacuum tubes which can control the flow of electronics in a vacuum. These tubes are usually used in switches, amplifiers, radios, televisions, etc. These computers were very heavy and large and were not ideal for programming. They used basic programming and didn’t have an operating system, which made it tough for users. These computers required a big room and consumed a lot of electricity.
The 2nd Generation of Computers used transistors instead of bulky vacuum tubes. Transistors, made from semiconductor materials, control current flow. This made the computers smaller, faster, and cooler. The computers introduced CPU, memory, and input/output units. Programming languages: FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), COBOL (1959).
The 3rd Generation used integrated circuits (ICs), made from silicon chips. These included transistors, registers, and capacitors. Programming languages like BASIC were introduced. This generation brought speed, reliability, and compact size.
From 1972 to 2010, computers used microprocessors — a chip containing all circuits for arithmetic, logic, and control. Computers became small and portable. Concepts like multiprocessing, time-sharing, virtual memory were introduced. Private computers and networks became a reality.
The Fifth Generation of Computers has been built using the technology called Artificial Intelligence (AI). This technology encourages computers to behave like humans.
Some applications of AI can be seen in features like voice recognition, entertainment, etc.
The speed of the Fifth Generation of Computers is the highest while the size is the smallest.
A big improvement has been noticed over the years in various generations of computers in aspects of speed, accuracy, dimensions, etc.
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as a case, CPU, RAM, monitor, and mouse which processes input and gives desired output.
These hardware components are divided into:
These allow user interaction with the computer, entering data or information.
These display the output of any task given to the computer in human-readable form.
Examples:CPU (Central Processing Unit), it is the brain of the computer. It is the part that does most of the work in a computer system. Just like how our brain controls our body and processes information, the CPU carries out instructions from programs and performs calculations. It’s made up of smaller components that work together to execute tasks, making it the heart of any computing device.
All types of data processing operations from simple arithmetic to complex tasks and all the important functions of a computer are performed by the CPU. It helps input and output devices to communicate with each other and perform their respective operations. It also stores data which is input, intermediate results in between processing, and instructions. The CPU’s job is to make sure everything runs smoothly and efficiently. In this article, we are going to discuss CPU in detail.
A Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the most important component of a computer system. A CPU is hardware that performs data input/output, processing, and storage functions for a computer system. A CPU can be installed into a CPU socket. These sockets are generally located on the motherboard. CPU can perform various data processing operations. It can store data, instructions, programs, and intermediate results. CPU works like the brain of the computer.
Now, the CPU consists of 3 major units, which are:

As the name suggests, this unit can store instructions, data, and intermediate results. The memory unit is responsible for transferring information to other units of the computer when needed. It is also known as internal storage unit, main memory, or primary storage or Random Access Memory (RAM).
Its size affects speed, power, and performance. There are two types of memory in the computer: primary memory and secondary memory. Some main functions of memory units are listed below:
As the name suggests, a control unit controls the operations of all parts of the computer but it does not carry out any data processing operations. Executing already stored instructions, it instructs the computer by using the electrical signals to instruct the computer system. It takes instructions from the memory unit and then decodes the instructions after that it executes those instructions. So, it controls the functioning of the computer. Its main task is to maintain the flow of information across the processor.
Some main functions of the control unit are listed below:
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) is responsible for performing arithmetic and logical functions or operations. It consists of two subsections, which are:
Memory is a storage part in a computer system. It is used to store the data, information, and programs at the time of processing on the computer. It stores data either temporarily or permanently. The main use of memory is saving and retrieving data.
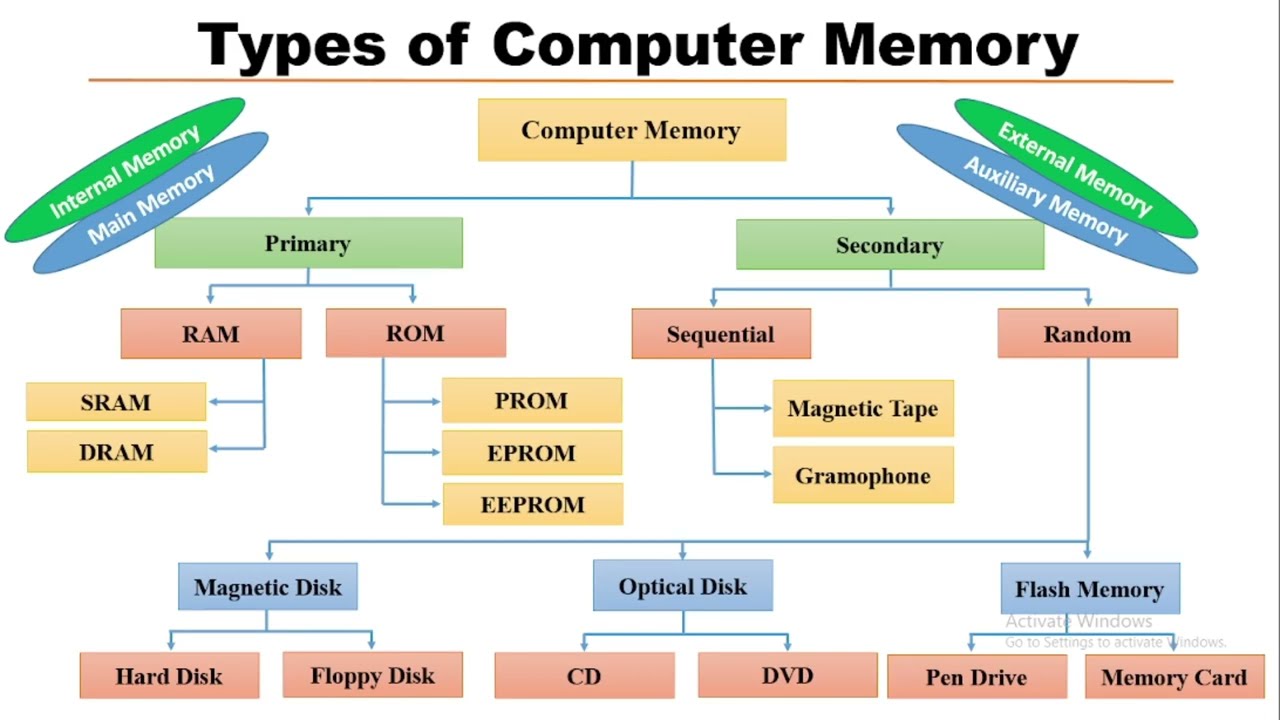
Generally, a computer system consists of two types of memory:
It is called the internal memory of the computer, also known as main memory or temporary memory. It holds data and instructions currently being used by the CPU.
Volatile memory loses all stored data when power is turned off.
Primary memory is generally of two types:
It is a read/write memory and referred as the main memory of the system. It is temporary, and the data is lost when the power is switched off.
Types of RAM:
ROM is a permanent type of memory. It does not lose data when power is turned off. Its content is written by the manufacturer and cannot be overwritten.
It is also called Non-Volatile Memory.
Types of ROM: