Raw, unprocessed facts or details without context or meaning. Data is unorganized and often collected from observations, measurements, or recordings.
Examples: Numbers, dates, text, images, or symbols that need interpretation (e.g., "25," "2023-09-04," or "John").
Processed, organized, or structured data that is meaningful and useful for decision-making or understanding. Information is data that has been interpreted, giving it context and significance.
Examples: A report showing the average temperature, a summarized sales report, or an analyzed dataset showing trends.
Record is the collection of various types of data of similar field.
Data file is the collection of record some time called table.
Persistent data is information that is stored in a way that it
remains available even after the system or device that created it is turned off or
restarted.
Persistent data doesn't disappear when you turn off your computer or close an
app. It's saved on storage devices like hard drives, SSDs, or databases.
Persistent data is crucial for things you need to keep over time, like files,
settings, or records in a business..
A database is an organized collection of data. The data can be anything from a list of names and phone numbers to detailed records of transactions in a company. Databases are structured to allow easy retrieval, insertion, updating, and deletion of data.
A file is a collection of data stored on a computer or other devices. Files can contain different types of data, such as text, images, videos, or software programs. Each file has a name and usually an extension that indicates the type of data it holds (e.g., .txt for text files, .jpg for images, .mp4 for videos).
A file management system is a software that helps you organize, store, retrieve, and manage files on your computer or device. It provides tools to perform tasks like:
You can create new files for storing information.
Files can be grouped into folders or directories, making them easier to find and manage.
You can open and make changes to the content of files.
Changes made to files can be saved to keep the information up to date.
You can remove files you no longer need.
The system allows you to search for files by name, type, or other criteria.
Important files can be copied to another location to prevent loss.
File structure refers to the way data is arranged within a file. This arrangement can vary depending on the file type, but it typically involves a combination of headers, metadata, and data content.
Typically organized as a sequence of lines, each ending with a newline character.
Often have a structured format, such as a relational database that stores data in tables with rows and columns.
File Structure refers to the way files are arranged on a storage device. This organization is often hierarchical, with files grouped into directories (or folders).
There are several types of file organization in database management systems (DBMS), each with its own advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific application requirements. Here are some of the most common types:
Records are stored in a sequential order based on a primary key.
Simple to implement and efficient for sequential access.
Inefficient for random access, insertions, and deletions.
Records are stored in a sequential order, but an index is maintained to provide efficient random access.
Efficient for both sequential and random access.
More complex to implement and requires additional storage for the index.
Records are stored based on a calculated address using a hashing function.
Very efficient for random access.
Can suffer from collisions, which can lead to inefficient access.
Records are grouped together based on a common attribute.
Efficient for queries involving the clustering attribute.
Less efficient for queries involving other attributes.
Similar to direct file organization, but uses a more complex hashing function to reduce collisions.
Very efficient for random access and has fewer collisions than direct file organization.
More complex to implement.
Uses multiple levels of indexes to provide efficient access to large datasets.
Can handle very large datasets efficiently.
More complex to implement and requires additional storage for the indexes.
It's like a digital librarian that helps you organize, store, and retrieve information efficiently. Imagine a library with countless books. A DBMS is the system that helps you find the exact book you need, even if it's buried among millions of others.
The DBMS stores data in a structured format, often using tables. Each table has rows (records) and columns (fields).
You can use the DBMS to add, delete, or modify data. For instance, you could add a new customer to the customer table.
The DBMS allows you to query the data to find specific information. For example, you could search for all customers living in a particular city.
The DBMS ensures that your data is protected from unauthorized access. It includes features like user authentication and data encryption.
DBMSs are designed to handle large amounts of data efficiently, making it easy to find and manage information.
DBMSs help maintain data consistency, ensuring that information is accurate and up-to-date.
DBMSs provide security features to protect your data from unauthorized access and corruption.
DBMSs allow multiple users to access and share data simultaneously.
Databases have been around for centuries, but the way we manage and interact with them has evolved significantly over time.
The earliest databases were physical records, like ledgers and card catalogs. Information was stored on paper or cards.
Data was accessed and updated manually, which was time-consuming and prone to errors.
The relational model, introduced by Edgar F. Codd in the 1970s, revolutionized database management. It represented data as tables, with rows and columns.
The Structured Query Language (SQL) was developed to interact with relational databases. It provided a standardized way to query, update, and manage data.
NoSQL databases, also known as "Not Only SQL," emerged to address the limitations of relational databases for large-scale, distributed applications. They offer flexibility, scalability, and high performance.
Document databases (e.g., MongoDB), key-value stores (e.g., Redis), wide-column databases (e.g., Cassandra), and graph databases (e.g., Neo4j) are common types of NoSQL databases.
The rise of cloud computing has led to the popularity of cloud-based databases. These databases are hosted and managed in the cloud, offering scalability, accessibility, and reduced maintenance costs.
A database is a structured collection of data. Here are some key characteristics:
Data is organized in a systematic manner, often using tables, rows, and columns.
Data can be related to each other through defined relationships, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many.
Databases maintain data integrity, ensuring that data is accurate, consistent, and free from errors.
Rules and constraints can be applied to validate data, preventing invalid or inconsistent entries.
Databases are designed to provide efficient access to data, allowing users to retrieve information quickly.
Indexes can be created to speed up data retrieval by organizing data in a specific way.
Databases implement access control mechanisms to protect data from unauthorized access.
Sensitive data can be encrypted to ensure confidentiality.
Databases often have built-in backup and recovery mechanisms to protect data from loss or corruption.
Data can be replicated to ensure availability in case of failures.
Databases can be scaled to accommodate increasing amounts of data and users.
Scalability ensures that the database can maintain performance as it grows.
Data independence allows changes to the physical storage of data without affecting the logical view of the data.
Databases support concurrent access, allowing multiple users to access and modify data simultaneously.
Mechanisms are in place to prevent conflicts and ensure data consistency.
Database approaches are the different strategies employed to organize, manage, and access data. Each approach has its own unique characteristics, which influence its suitability for various applications. Here are some of the key characteristics to consider:
Data is organized into tables, where each table represents an entity (e.g., customer, order). Tables are linked using relationships (e.g., one-to-one, one-to-many).
Combines features of relational and object-oriented databases.
Offers various data models such as document, key-value, graph, and wide-column.
Ensures that all copies of data are always identical.
Data may be temporarily inconsistent, but eventually all copies will converge.
Provides no guarantees about data consistency.
The ability to add more nodes to a distributed system to handle increased load.
The ability to increase the capacity of a single node to handle increased load.
How quickly the DBMS can execute queries.
How quickly the DBMS can process transactions.
How well the DBMS handles concurrent access to data.
How easily the DBMS can accommodate changes to the data structure.
How well the DBMS can handle different types of data (e.g., structured, semi-structured, unstructured).
The ability of the DBMS to continue functioning even if components fail.
The ability of the DBMS to protect data from loss in the event of a system failure.
The ability to restrict access to data based on user roles and permissions.
The ability to encrypt data to protect it from unauthorized access.
The cost of obtaining and using the DBMS software.
The cost of the hardware required to run the DBMS.
The cost of maintaining and updating the DBMS.
A DBMS is like a digital librarian that helps you organize, store, and retrieve information efficiently. It consists of several key components:
This is the raw information you want to store, like customer details, product information, or sales records.
This is the blueprint or structure of the data. It defines how the data is organized and related to each other.
This is the actual DBMS system, which provides tools to interact with the data. It includes features like data entry, retrieval, and modification.
This refers to the physical components of the system, such as servers, storage devices, and networking equipment.
These are the people who interact with the DBMS. They can be database administrators, developers, or end-users.
These are the rules and guidelines that govern how the DBMS is used. They include things like data security protocols and backup procedures.
It can control data redundancy because it stores all the data in one single database file and that recorded data is placed in the database.
In DBMS, the authorized users of an organization can share the data among multiple users.
It can be easily maintainable due to the centralized nature of the database system.
It reduces development time and maintenance need.
It provides backup and recovery subsystems which create automatic backup of data from hardware and software failures and restores the data if required.
It provides different types of user interfaces like graphical user interfaces, application program interfaces
It requires a high speed of data processor and large memory size to run DBMS software.
It occupies a large space of disks and large memory to run them efficiently.
Database system creates additional complexity and requirements.
Failure is highly impacted the database because in most of the organization, all the data stored in a single database and if the database is damaged due to electric failure or database corruption then the data may be lost forever.
| Basics | File System | DBMS |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | The file system is a way of arranging the files in a storage medium within a computer. | DBMS is software for managing the database. |
| Data Redundancy | Redundant data can be present in a file system. | In DBMS there is no redundant data. |
| Backup and Recovery | It doesn’t provide inbuilt mechanism for backup and recovery of data if it is lost. | It provides in house tools for backup and recovery of data even if it is lost. |
| Query processing | There is no efficient query processing in the file system. | Efficient query processing is there in DBMS. |
| Consistency | There is less data consistency in the file system. | There is more data consistency because of the process of normalization. |
| Complexity | It is less complex as compared to DBMS. | It has more complexity in handling as compared to the file system. |
| Security Constraints | File systems provide less security in comparison to DBMS. | DBMS has more security mechanisms as compared to file systems. |
| Cost | It is less expensive than DBMS. | It has a comparatively higher cost than a file system. |
| User Access | Only one user can access data at a time. | Multiple users can access data at a time. |
| Sharing | Data is distributed in many files. So, it is not easy to share data. | Due to centralized nature data sharing is easy. |
| Attributes | To access data in a file, user requires attributes such as file name, file location. | No such attributes are required. |
| Example | Cobol, C++ | Oracle, SQL Server |
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software application that helps you manage data efficiently. To use a DBMS, there are different types of users, each with specific roles and responsibilities.
The primary person responsible for managing the DBMS.
Responsibilities:Create software applications that interact with the database.
Responsibilities:People who use the applications created by developers to access and manipulate data.
Responsibilities:Analyze data to extract meaningful insights.
Responsibilities:Responsible for the overall IT infrastructure, including the DBMS.
Responsibilities:Imagine a bank. The DBA would be responsible for creating and maintaining the bank's database, ensuring data security, and optimizing performance. The application developers would create the online banking system. End users would be the customers who use the online banking system to check balances, transfer funds, and pay bills. Data analysts would analyze customer behavior to identify trends and improve marketing strategies. System administrators would ensure the overall stability and security of the bank's IT infrastructure, including the DBMS.
A Database store a lot of critical information to access data quickly and securely. Hence it is important to select the correct architecture for efficient data management. DBMS Architecture helps users to get their requests done while connecting to the database. We choose database architecture depending on several factors like the size of the database, number of users, and relationships between the users. There are two types of database models that we generally use, are logical model and physical model.
There are several types of DBMS Architecture that we use according to the usage requirements. Types of DBMS Architecture are discussed here.
In 1-Tier Architecture the database is directly available to the user, the user can directly sit on the DBMS and use it that is, the client, server, and Database are all present on the same machine. For Example: to learn SQL we set up an SQL server and the database on the local system. This enables us to directly interact with the relational database and execute operations. The industry won’t use this architecture they logically go for 2-Tier and 3-Tier Architecture.

Simple Architecture: 1-Tier Architecture is the most simple architecture to set up, as only a single machine is required to maintain it.
Cost-Effective: No additional hardware is required for implementing 1-Tier Architecture, which makes it cost-effective.
Easy to Implement: 1-Tier Architecture can be easily deployed, and hence it is mostly used in small projects.
The 2-tier architecture is similar to a basic client-server model. The application at the client end directly communicates with the database on the server side. APIs like ODBC and JDBC are used for this interaction. The server side is responsible for providing query processing and transaction management functionalities. On the client side, the user interfaces and application programs are run. The application on the client side establishes a connection with the server side in order to communicate with the DBMS. An advantage of this type is that maintenance and understanding are easier, and compatible with existing systems. However, this model gives poor performance when there are a large number of users.
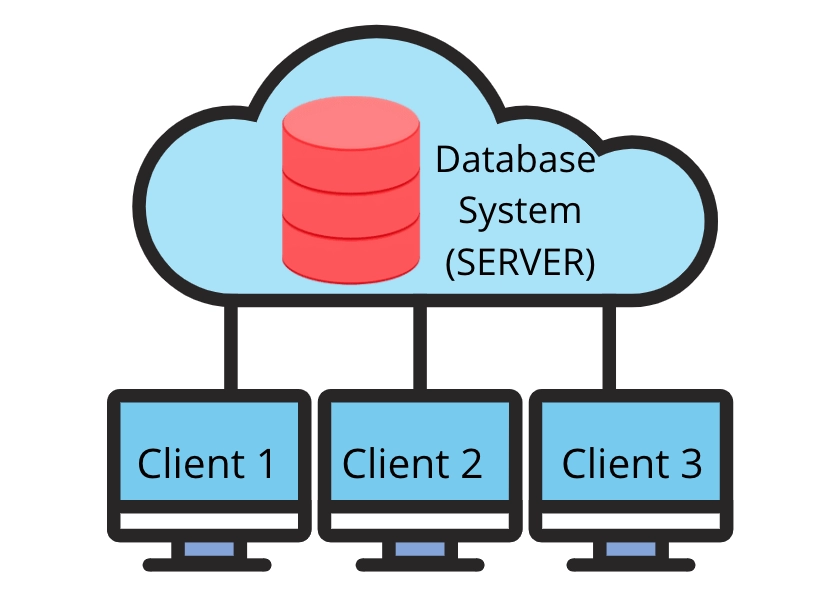
Easy to Access: 2-Tier Architecture makes easy access to the database, which makes fast retrieval.
Scalable: We can scale the database easily, by adding clients or by upgrading hardware.
Low Cost: 2-Tier Architecture is cheaper than 3-Tier Architecture and Multi-Tier Architecture.
Easy Deployment: 2-Tier Architecture is easy to deploy than 3-Tier Architecture.
Simple: 2-Tier Architecture is easily understandable as well as simple because of only two components.
In 3-Tier Architecture, there is another layer between the client and the server. The client does not directly communicate with the server. Instead, it interacts with an application server which further communicates with the database system and then the query processing and transaction management takes place. This intermediate layer acts as a medium for the exchange of partially processed data between the server and the client. This type of architecture is used in the case of large web applications.