Introduction
Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable. The effectiveness of a data communications system depends on four fundamental characteristics: delivery, accuracy, timeliness and jitter.
Characteristics
- Delivery: Data must be received by the intended device or user.
- Accuracy: Data must be accurate and unchanged.
- Timeliness: Data must be delivered on time.
- Jitter: Uneven delay in the delivery of audio/video packets.
Components
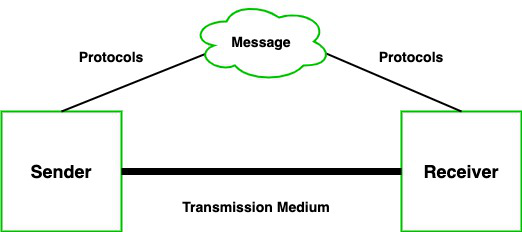
A data communications system has five components:
- Message: The data to be communicated (text, number, audio, video, etc.).
- Sender: The device that sends the message (e.g., computer, workstation).
- Receiver: The device that receives the message.
- Transmission medium: The physical path (e.g., twisted-pair, fiber-optic, radio waves).
- Protocol: A set of rules governing communication between devices.
Communication Flow Diagram
Data communication system diagram
Transmission modes
- The way in which data is transmitted from one device to another device is known as transmission mode.
- The transmission mode is also known as the communication mode.
- Each communication channel has a direction associated with it, and transmission media provide the direction. Therefore, the transmission mode is also known as a directional mode.
- The transmission mode is defined in the physical layer.
The Transmission mode is divided into three categories:
- Simplex mode
- Half-duplex mode
- Full-duplex mode
Simplex mode

- In Simplex mode, the communication is unidirectional, i.e., the data flow in one direction.
- A device can only send the data but cannot receive it or it can receive the data but cannot send the data.
- This transmission mode is not very popular as mainly communications require the two-way exchange of data.
- The simplex mode is used in the business field as in sales that do not require any corresponding reply.
- The radio station is a simplex channel as it transmits the signal to the listeners but never allows them to transmit back.
- Keyboard and Monitor are the examples of the simplex mode as a keyboard can only accept the data from the user and monitor can only be used to display the data on the screen.
- The main advantage of the simplex mode is that the full capacity of the communication channel can be utilized during transmission.
Advantage of Simplex mode:
- In simplex mode, the station can utilize the entire bandwidth of the communication channel, so that more data can be transmitted at a time.
Disadvantage of Simplex mode:
- Communication is unidirectional, so it has no inter-communication between devices.
Half-Duplex mode
- In a Half-duplex channel, direction can be reversed, i.e., the station can transmit and receive the data as well.
- Messages flow in both the directions, but not at the same time.
- The entire bandwidth of the communication channel is utilized in one direction at a time.
- In half-duplex mode, it is possible to perform the error detection, and if any error occurs, then the receiver requests the sender to retransmit the data.
- A Walkie-talkie is an example of the Half-duplex mode. In Walkie-talkie, one party speaks, and another party listens. After a pause, the other speaks and first party listens. Speaking simultaneously will create the distorted sound which cannot be understood.
Advantage of Half-duplex mode:
- In half-duplex mode, both the devices can send and receive the data and also can utilize the entire bandwidth of the communication channel during the transmission of data.
Disadvantage of Half-Duplex mode:
- In half-duplex mode, when one device is sending the data, then another has to wait, this causes the delay in sending the data at the right time.
Full-duplex mode

- In Full duplex mode, communication is bi-directional, i.e., the data flow in both the directions.
- Both the stations can send and receive the message simultaneously.
- This mode is the fastest mode of communication. One channel has traffic moving in one direction, and another channel has traffic flowing in the opposite direction.
- Full-duplex mode is the fastest mode of communication between devices.
- The most common example of the full-duplex mode is a telephone network. When two people are communicating with each other by a telephone line, both can talk and listen at the same time.
Advantage of Full-duplex mode:
- Both the stations can send and receive the data at the same time.
Disadvantage of Full-duplex mode:
- If there is no dedicated path exists between the devices, then the capacity of the communication channel is divided into two parts.
Difference Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission
In the world of computers and communication, how information travels from one place to another can happen in different ways. Two common methods are synchronous and asynchronous transmission. In this article, we are going to discuss the difference between synchronous and asynchronous transmission in detail.
What is Synchronous Transmission?
In Synchronous Transmission, data is sent in the form of blocks or frames. This transmission is the full-duplex type. Between sender and receiver, synchronization is compulsory. There is no time gap present between data. It is more efficient and more reliable than asynchronous transmission to transfer a large amount of data.
Both the sender and receiver are synchronized with a common clock signal. This means they operate at the same speed and know exactly when to send and receive data. Data is sent in a continuous stream, with each byte or chunk of data following the previous one without any gaps. It’s efficient for large amounts of data because there’s less overhead (extra bits) needed to start and stop the transmission.
Example:
- Chat Rooms
- Telephonic Conversations
- Video Conferencing
What is Asynchronous Transmission?
In Asynchronous Transmission, data is sent in form of byte or character. This transmission is the half-duplex type. Start bits and stop bits are added with data. It does not require synchronization. Asynchronous transmission is like sending individual text messages without knowing exactly when the other person will read them.
The sender and receiver do not share a common clock signal. Instead, data is sent one byte or character at a time, with start and stop bits indicating the beginning and end of each byte. Each piece of data is sent independently, with gaps in between, allowing the receiver to process each byte as it arrives. It’s flexible and simpler to implement, especially useful for communications where data is sent intermittently.
Example:
- Forums
- Letters
Transmission medium
- can be broadly defined as anything that can carry information from a source to a destination.

Guided Media
: Guided media, which are those that provide a medium from one device to another, include twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable.
Twisted-Pair Cable

- A twisted pair consists of two conductors (normally copper), each with its own plastic insulation, twisted together. One of the wires is used to carry signals to the receiver, and the other is used only as a ground reference.
Unshielded Versus Shielded Twisted-Pair Cable
- The most common twisted-pair cable used in communications is referred to as unshielded twisted-pair (UTP).
- STP cable has a metal foil or braided mesh covering that encases each pair of insulated conductors.
- Although metal casing improves the quality of cable by preventing the penetration of noise or crosstalk, it is bulkier and more expensive.
- The most common UTP connector is RJ45 (RJ stands for registered jack).
Applications
- Twisted-pair cables are used in telephone lines to provide voice and data channels.
- Local-area networks, such as 10Base-T and 100Base-T, also use twisted-pair cables.
Unshielded Versus Shielded Twisted-Pair Cable
- The most common twisted-pair cable used in communications is referred to as unshielded twisted-pair (UTP). STP cable has a metal foil or braided mesh covering that encases each pair of insulated conductors.
- The most common UTP connector is RJ45 (RJ stands for registered jack).
Applications
- Twisted-pair cables are used in telephone lines to provide voice and data channels.
- Local-area networks, such as 10Base-T and 100Base-T, also use twisted-pair cables.
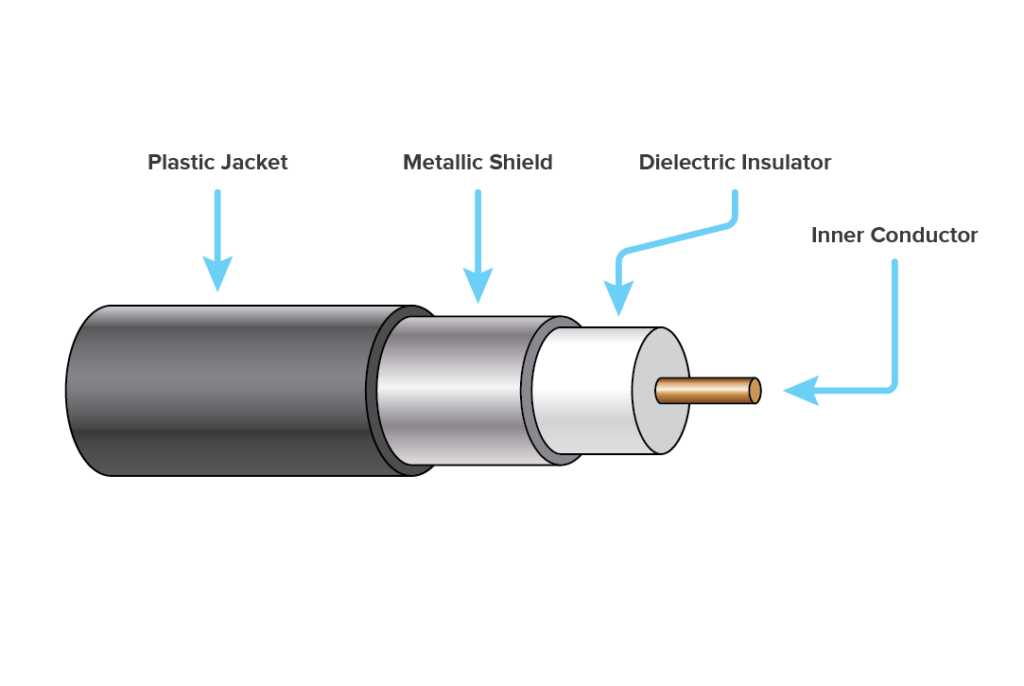
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable (or coax) carries signals of higher frequency ranges than those in twisted pair cable.
Applications
- Coaxial cable was widely used in analog telephone networks, digital telephone networks.
- Cable TV networks also use coaxial cables.
- Another common application of coaxial cable is in traditional Ethernet LANs.
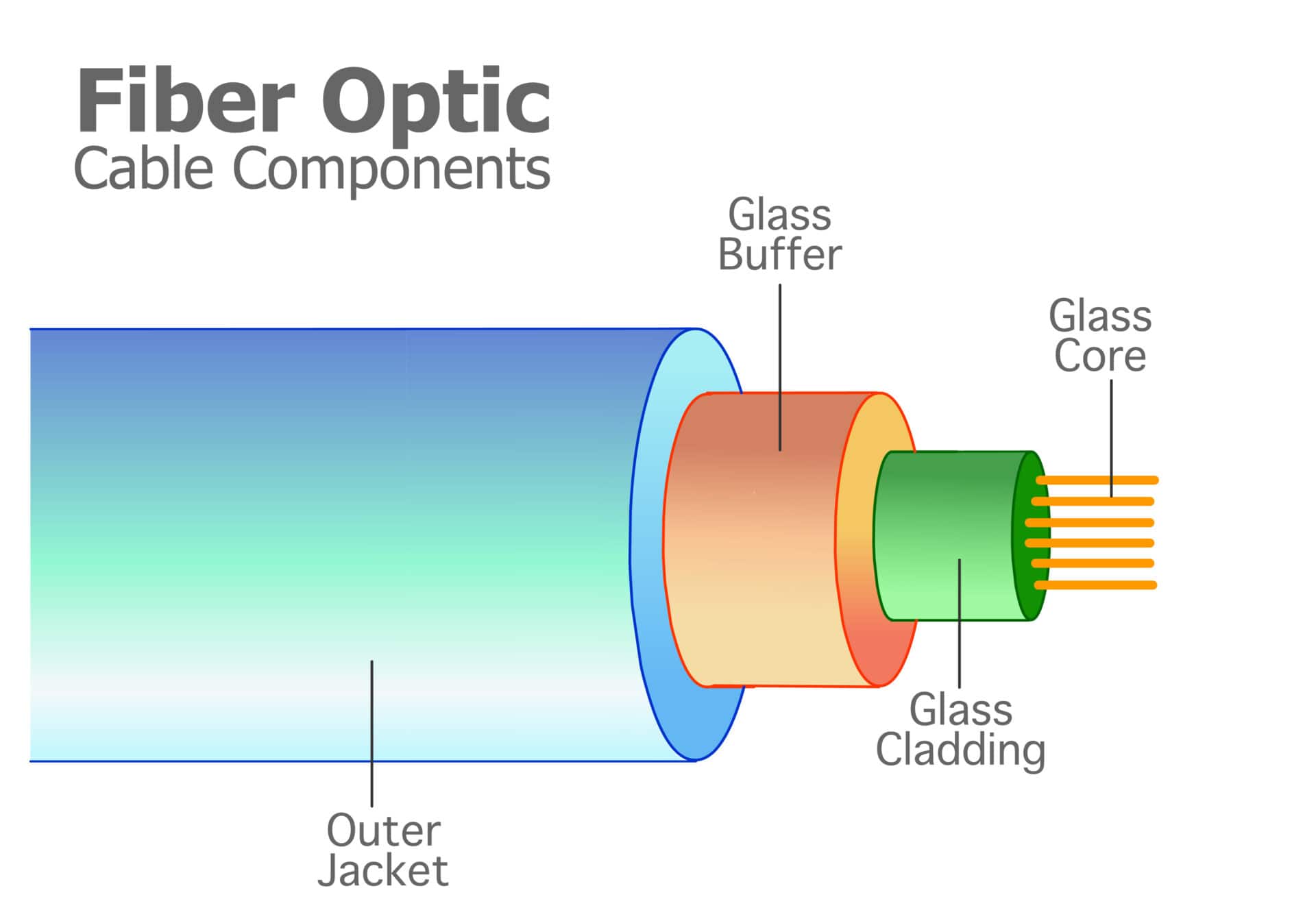
Fiber-Optic Cable
- A fiber-optic cable is made of glass or plastic and transmits signals in the form of light.
- Light travels in a straight line as long as it is moving through a single uniform substance.
- If a ray of light traveling through one substance suddenly enters another substance (of a different density), the ray changes direction. Bending of light ray
- Optical fibers use reflection to guide light through a channel. A glass or plastic core is surrounded by a cladding of less dense glass or plastic.
Unguided Media: Wireless
Unguided media transport electromagnetic waves without using a physical conductor. This type of communication is often referred to as wireless communication.
- Radio Waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared
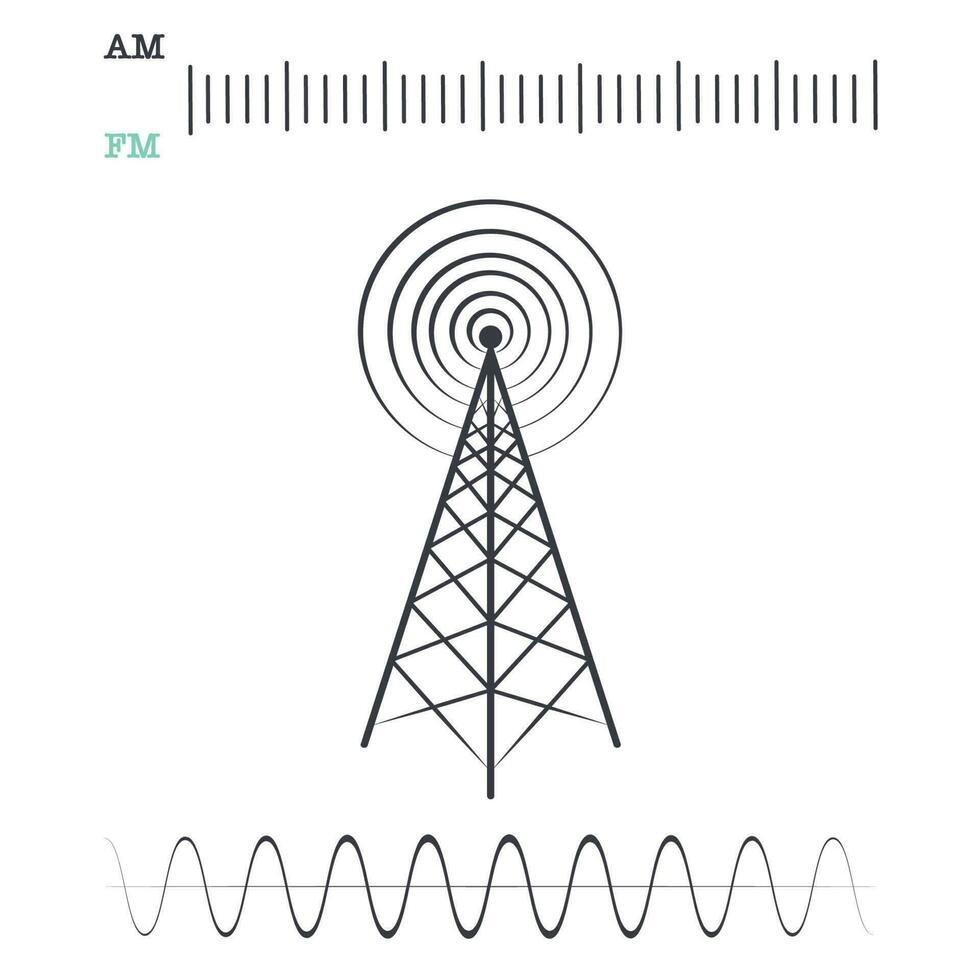
📻 Radio Waves
Electromagnetic waves ranging in frequencies between 3 kHz and 1 GHz are normally called radio waves.
- Radio waves are omni directional. When an antenna transmits radio waves, they are propagated in all directions. This means that the sending and receiving antennas do not have to be aligned.
Applications:
The omnidirectional characteristics of radio waves make them useful for multicasting, in which there is one sender but many receivers.
Examples: AM and FM radio, television, maritime radio, cordless phones, and paging.
📡 Microwaves
Electromagnetic waves having frequencies between 1 and 300 GHz are called microwaves.
- Microwaves are unidirectional. The sending and receiving antennas need to be aligned.
Applications:
Microwaves are used for unicast communication such as:
Cellular telephones, satellite networks, and wireless LANs.

Dish Antenna
🌈 Infrared
Infrared waves, with frequencies from 300 GHz to 400 THz (wavelengths from 1 mm to 770 nm), can be used for short-range communication. Infrared waves, having high frequencies, cannot penetrate walls.
Applications:
Infrared signals can be used for short-range communication in a closed area using line-of-sight propagation.
Computer Network
A computer network is an interconnected collection of autonomous computers able to exchange information. A computer network is a set of devices connected through links. A node can be computer, printer, or any other device capable of sending or receiving the data. The links connecting the nodes are known as communication channels. Computer Network uses distributed process computers. Instead, a single computer handles an entire task, each separate computer handles a subset.
Internet being the most well-known example of a network of networks.
Goal of Computer Network
Communication speed
Network provides us to communicate over the network in a fast and efficient manner. For example, we can do video conferencing, email messaging, etc. over the internet. Therefore, the computer network is a great way to share our knowledge and ideas.
File sharing
File sharing is one of the major advantages of the computer network. It provides us the ability to share files with each other easily.
Back up and Roll back
Since the files are stored in the main server, it is easy to take back up from the server centrally.
Software and Hardware Sharing
We can install the applications on the main server, therefore, the user can access the applications centrally. So, we do not need to install the software on every machine. Similarly, hardware can also be shared.
Security
Network allows the security by ensuring that the user has the right to access the certain files and applications.
Scalability
Scalability means that we can add the new components on the network. Network must be scalable so that we can extend the network by adding new devices. But, it decreases the speed of the connection and data of the transmission speed also decreases, this increases the chances of error occurring. This problem can be overcome by using the routing or switching devices.
Reliability
Computer network can use the alternative source for the data communication in case of any hardware failure.Uses of Computer Networks
Had it not been of high importance, nobody would have bothered connecting computers over a network. Let's start exploring the uses of Computer Networks with some traditional use cases at companies and for individuals and then move on to the recent developments in the area of mobile users and home networking.
Computer Networks: Business Applications
Following are some business applications of computer networks:
1. Resource Sharing:
The goal is to make all programs, equipments (like printers etc), and especially data, available to anyone on the network without regard to the physical location of the resource and the user.
2. Server-Client model:
One can imagine a company’s information system as consisting of one or more databases and some employees who need to access it remotely. In this model, the data is stored on powerful computers called Servers. Often these are centrally housed and maintained by a system administrator. In contrast, the employees have simple machines, called Clients, on their desks, using which they access remote data.
3. Communication Medium:
A computer network can provide a powerful communication medium among employees. Virtually every company that has two or more computers now has e-mail (electronic mail), which employees generally use for a great deal of daily communication.
4. eCommerce:
A goal that is starting to become more important in businesses is doing business with consumers over the Internet. Airlines, bookstores, and music vendors have discovered that many customers like the convenience of shopping from home. This sector is expected to grow quickly in the future.
Computer Networks: Home Applications
Computer Networks: Home Applications
Some of the most important uses of the Internet for home users are as follows:
- Access to remote information
- Person-to-person communication
- Interactive entertainment
- Electronic commerce
Computer Networks: Mobile Users
Mobile computers, such as notebook computers and mobile phones, are one of the fastest-growing segments of the entire computer industry.
Difference Between Point-to-Point and Multi-Point Communication
Communication, as we all know, is the process of sending information from a source to a destination using any available media like audio, video, signal, or even text. This communication could be simple, including only one sender and one receiver, or it could involve several senders and receivers. We can distinguish between Point-to-Point and Multi-Point communication based on the number of senders and receivers in a communication.
Point-to-Point Communication
A point-to-point communication is also known as P2P. In the context of telecommunication, it is an established connection between two nodes that may be used to communicate back and forth.
These P2P connections were first established using circuit-switched landlines. Modern versions use complex fibre-optic networks. P2P communication can transmit various types of data, including digital and analog signals.
It is a unicast connection, where a dedicated link exists between sender and receiver. The entire channel is reserved solely for packet transmission.
Multipoint Communication
In multipoint communication, the link is shared among multiple devices. Instead of a dedicated path, the communication media is divided or accessed either spatially or in time slots by multiple devices. As a result, this type of connection is more efficient in terms of resource usage, but may involve delay.
